The
Two Alike, the Two Similar, the Two Close, and the Two Far

The
meeting of two letters is of three different ways:
1.
Meeting of the two in pronunciation and writing, in that there is no
separation between them, such as the two
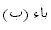 in
in
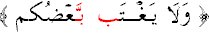 and
the two
and
the two
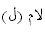 in
in
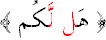 .
.
2.
Meeting of the two in writing only, such as in :
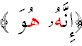 .
Here the two
.
Here the two
 are
next to each other, but
are
next to each other, but
 prevents
them from being pronounced together, by the way we read (
prevents
them from being pronounced together, by the way we read (

3.
Meeting of the two in pronunciation only, as in
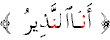 .
In this case the alif separates the two
.
In this case the alif separates the two
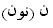 from each other, but since the alif is not pronounced, the two
from each other, but since the alif is not pronounced, the two
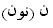 meet in pronunciation.
meet in pronunciation.
The
first type is what will be discussed in this and subsequent lessons; the
second and third type do not enter this section or do not apply to the way we
read. When discussing the relationship of two letter that meet, it does
not matter whether they meet in one word or are in two different words, and
the letters meet each other by one being at the end of a word and the other at
the beginning of the next word.
The
study of the relationships between letters is important to learn which letters
can merge with others and under which circumstances.
The
relationship between two meeting letters is divided into four divisions:
1.
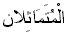 The
Two Like Each Other
The
Two Like Each Other
2.
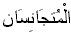 The Two of the
Same Nature as Each Other
The Two of the
Same Nature as Each Other
3.
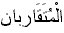 The
Two Approximates to Each Other
The
Two Approximates to Each Other
4.
 The Two Far
from Each Other
The Two Far
from Each Other
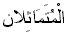 The Two Like Each Other
The Two Like Each Other
Its
Definition: They are the two
letters that are the same in characteristic and in articulation point.. This
means they are the exact same letters next to each other. Examples of this
are: The two
 in
in
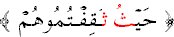 ,
or the two
,
or the two
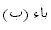 in
:
in
:
 , or the two
, or the two
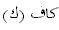 in
in
 .
.
There
is an exception to this rule when two
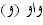 and
two
and
two
 are
next to each other in writing, but one of the two
are
next to each other in writing, but one of the two
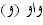 and
one of the two
and
one of the two
 are
a medd letter such as in
are
a medd letter such as in
 and
and
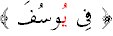 .
In the first example:
.
In the first example:
 the
the
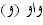 of
the word
of
the word
 is a medd letter. The
first
is a medd letter. The
first
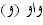 of the word
of the word
 is not a medd letter. In
the second example:
is not a medd letter. In
the second example:
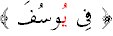 , the
, the
 of
the word
of
the word
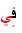 is a medd letter, so we the
have a natural lengthening, the next letter following this
is a medd letter, so we the
have a natural lengthening, the next letter following this
 is
a
is
a
 with a vowel on it,
with a vowel on it,
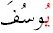 .
We then apply this exception of medd letters not merging into non-medd
letters of the same type, and do not merge (make of
.
We then apply this exception of medd letters not merging into non-medd
letters of the same type, and do not merge (make of
 of ) the two letters.
This is in contrast to the
of ) the two letters.
This is in contrast to the
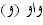 or
or
 saakinah
of
saakinah
of
 which
are followed by a
which
are followed by a
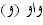 or
or
 with a vowel, such as
in:
with a vowel, such as
in:

 .
In this case there is
.
In this case there is
 of
the two letters that are the same (here, a
of
the two letters that are the same (here, a
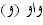 ).
).
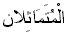 ,
or the two alike, has three divisions:
,
or the two alike, has three divisions:
-
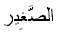 The Small
The Small
-
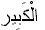 The Large
The Large
-
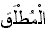 The
Absolute
The
Absolute
We
will continue, discussing these different divisions of
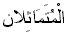 and their application, insha’ Allah, next
lesson.
and their application, insha’ Allah, next
lesson.
